In today’s digital landscape, securing your website is not an option—it’s a necessity. One of the fundamental aspects of online security is obtaining an SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificate. With multiple types of SSL certificates available, choosing the right one for your website can be overwhelming. This guide will walk you through the key factors to consider and help you determine the best SSL certificate for your needs.
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| What is an SSL Certificate? | Encrypts data between a website and users, ensuring security and trust. |
| Types of SSL Validation |
|
| SSL for Multiple Domains |
|
| Choosing a Certificate Authority (CA) | Pick a trusted CA like Let’s Encrypt, DigiCert, GlobalSign, Comodo, or Sectigo. |
| Browser & Mobile Compatibility | Ensure the SSL certificate is recognized by all major browsers and mobile devices. |
| Warranty & Support | Look for SSL certificates with warranties and 24/7 customer support. |
| SSL Certificate Cost |
|
Understanding SSL Certificates
An SSL certificate encrypts data transferred between a user’s browser and your website, ensuring security and preventing cyber threats like hacking and data breaches. Websites with an SSL certificate display HTTPS in their URL and show a padlock icon in the address bar, signaling a secure connection.
SSL certificates also play a role in SEO rankings, as search engines like Google prioritize secure websites in their results. Additionally, they are essential for gaining customer trust, especially for e-commerce and business websites handling sensitive data.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an SSL Certificate
Selecting the right SSL certificate depends on various factors, including your website’s size, type, and security requirements. Here are key considerations to keep in mind:
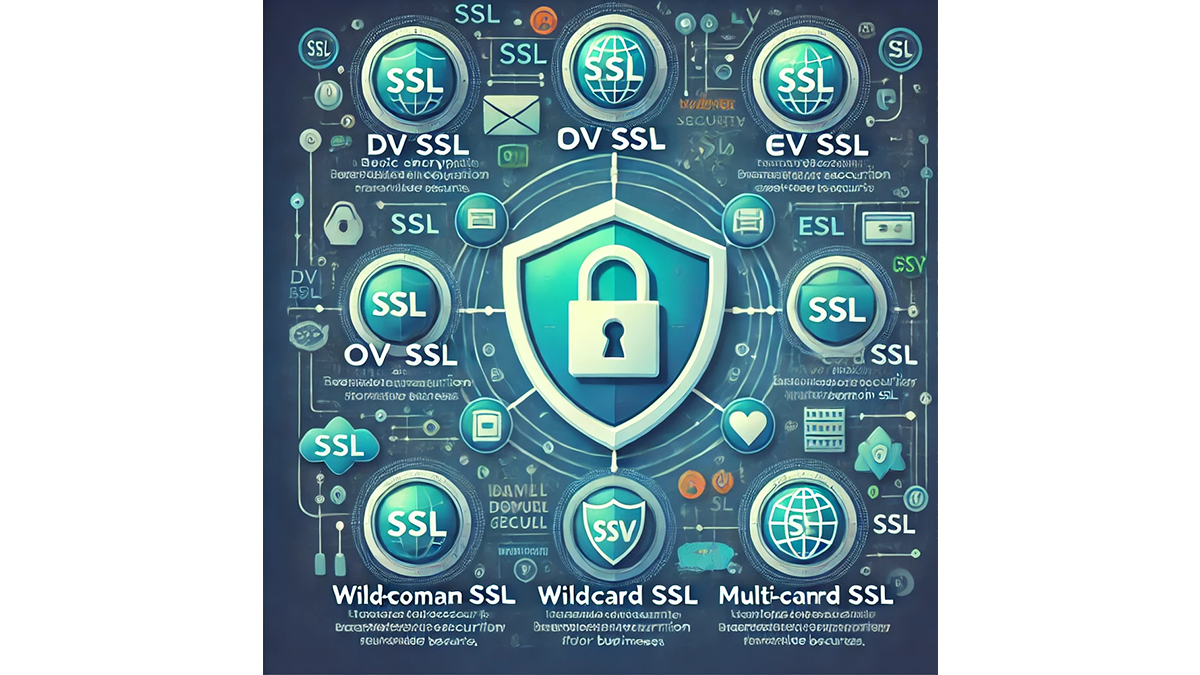
1. Determine Your Validation Level
SSL certificates come in three levels of validation:
- Domain Validation (DV) SSL
- Verifies domain ownership only.
- Provides basic encryption but does not validate business identity.
- Ideal for personal blogs and small informational websites.
- Organization Validation (OV) SSL
- Requires business verification.
- Displays company details in the certificate, boosting credibility.
- Recommended for small to medium businesses.
- Extended Validation (EV) SSL
- Involves the highest level of authentication.
- Provides a green address bar (in some browsers) for increased trust.
- Best for large businesses, financial institutions, and e-commerce platforms.
2. Assess the Number of Domains and Subdomains
If you manage multiple domains or subdomains, you need an SSL certificate that covers all of them efficiently. Here are your options:
- Single-Domain SSL: Protects only one specific domain (e.g., example.com). Best for personal websites or small businesses.
- Wildcard SSL: Secures a main domain and unlimited subdomains (e.g., example.com, blog.example.com, shop.example.com). Ideal for businesses with multiple subdomains.
- Multi-Domain SSL (MDC): Covers multiple domain names under one certificate (e.g., example.com, example.net, example.org). Suitable for companies managing several websites.
3. Identify Your Website Type and Purpose
- E-commerce Websites: Require high security to protect customer payment details. EV SSL is highly recommended.
- Business or Corporate Websites: OV or EV SSL enhances trust by displaying verified company details.
- Personal Blogs or Informational Sites: DV SSL provides sufficient security at a lower cost.
- Websites Handling Sensitive Data: Banks, healthcare institutions, and legal sites should use EV SSL for maximum security.
4. Consider the Certificate Authority (CA)
SSL certificates are issued by trusted Certificate Authorities (CAs) such as:
- Let’s Encrypt (free, but only provides DV SSL)
- DigiCert
- GlobalSign
- Comodo
- Sectigo
Choose a reputable CA to ensure reliability and strong encryption standards.
5. Check Browser and Mobile Compatibility
A good SSL certificate should be recognized by all major browsers and mobile devices. Ensure your chosen certificate offers broad compatibility to avoid security warnings for visitors.
6. Evaluate the Warranty and Support Options
Most premium SSL certificates include a warranty that compensates users in case of a security failure. Additionally, consider a provider that offers 24/7 customer support to assist with installation and troubleshooting.
7. Budget Considerations
SSL certificate prices vary based on validation level and coverage:
- Free SSL (Let’s Encrypt): Suitable for blogs and personal websites with minimal security needs.
- DV SSL (Affordable, $10-$50 per year): Ideal for small websites.
- OV SSL ($50-$200 per year): Suitable for businesses needing verified security.
- EV SSL ($200-$1,000 per year): Recommended for high-trust industries.
- Wildcard or Multi-Domain SSL (Can range from $100 to $1,500 per year): Suitable for businesses managing multiple domains.
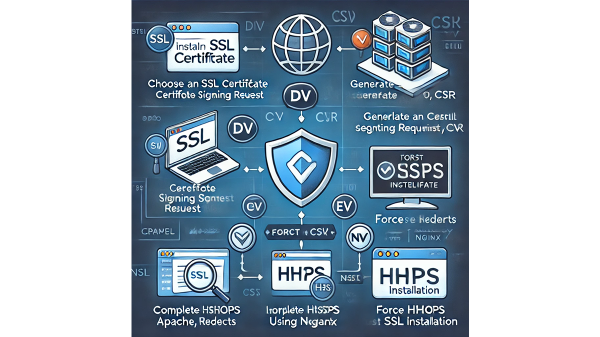
Steps to Obtain and Install an SSL Certificate
Once you’ve selected the right SSL certificate, follow these steps:
- Purchase or obtain a free SSL certificate from a trusted CA or your web hosting provider.
- Generate a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) from your web hosting control panel.
- Complete the validation process based on the type of SSL chosen.
- Receive and install the SSL certificate on your web server.
- Update website links to HTTPS and configure redirects.
- Test SSL installation using tools like SSL Labs’ SSL Test.
Conclusion
Choosing the right SSL certificate is essential for securing your website, improving trust, and enhancing SEO rankings. By assessing your website’s needs, validation level, and budget, you can select the best SSL certificate for your business or personal site. Whether you need a basic DV SSL or a high-security EV SSL, ensuring your website is encrypted will protect your data and boost user confidence.
If you haven’t secured your website yet, now is the time to invest in the right SSL certificate to keep your visitors safe and your business reputable.